Detailed Design Principles of High-Performance HMI Displays
Channel: RealPars
Category: Education
Tags: what is hmi displayhigh-performance hmihigh-performance hmi level 1high performance hmi handbookdetailed design principles of high-performance hmi displayshmi panelhmi graphics standardshmi displayhigh-performance hmi display hierarchieshmi level 4hmi screen designhmi display pricehigh-performance hmi standardshmi level 3hmi level 2information-based displayhmi displayshmi display hierarchiesdetailed design principles of high-performance hmi
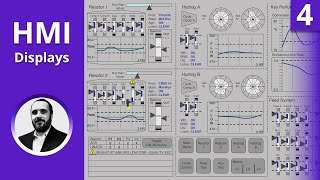
Description: ▶ C'mon over to realpars.com where you can learn PLC programming faster and easier than you ever thought possible! ============================= ▶ Check out the full blog post over at realpars.com/hmi-display ============================= If you need HMIs for your projects, you can easily order them online from the RealPars marketplace: marketplace.realpars.com/collections/hmi ============================= ⌚Timestamps: 00:00 - Intro 00:34 - High-Performance HMI hierarchy 01:17 - Level 1 02:09 - Level 2 02:56 - Layout and P&ID 03:22 - Level 3 04:20 - Level 4 04:53 - Pop-up display ============================= Welcome back to our series of What is High-Performance HMI? In this installment of the series, we are going to talk about the detailed design of a High-Performance HMI. A well-designed High-Performance HMI will generally consist of four display hierarchies: - Level 1, Process area Overview; - Level 2, Process Unit Control; - Level 3, Process Unit Detail; - Level 4, Process Unit Support. Each display will generate more detail and zoom in on the process. The philosophy behind the display levels is to give the operator the information that they are looking for without having data all over one or two different screens. 1) Your project will start with the Level 1 Display, and its primary purpose is to give the operators the broadest view or the big picture view of the plant or facility. A well-designed Level 1 display will give clear information of the current state of the process along with Key Performance Indicators such as production levels, process efficiency, and safety items. Most times, Level 1 displays will not have many graphics but will be more information-based and give the operator easy navigation to Level 2 displays. It will also give the indication of major upstream and downstream processes and finally will provide visual indications of abnormal situations and alarms. 2) Level 2 displays should include the information and controls that are required to perform most tasks on the particular process that was called from Level 1. Accessing Level 2 from Level 1 is a one-click operation. The purpose of Level 2 is to provide a clear picture of the systems in the process selected from Level 1. Once in Level 2, the operator now has the ability to operate process equipment such as pumps, valves, and compressors. While it is important to follow the physical layout of the facility and the P&ID, Level 2 screens should not look like a copy of the P&ID. 3) Moving on to a Level 3 display will provide detailed views and information from the Level 2 compressor display such as runtime, faults, alarms, commanded speed, and speed feedback. It could also include a custom trend showing process values such as pressure or flow. A Level 3 display will also include detailed diagnostic displays and interlocks. Detailed Level 3 displays are intended for advanced control and troubleshooting, items that are not available on Level 1 or Level 2. Many Level 3 displays may be accessible from a Level 2 display. 4) Level 4 Displays are obviously going to provide the greatest detail of sensors, subsystems, and individual components. In some cases, a Level 4 Display will provide information on PLC processor performance and the health of Input and Output channels. This display is meant for extensive and advanced troubleshooting, interlock programming, and process setpoint adjustments. You will also be able to view operating procedures, alarm response instructions, and abnormal situation response guidance. When possible, use a pop-up by utilizing a right mouse click on the alarm to provide a highly detailed and information-driven display that will give the operator clear instructions on the alarm and how to effectively troubleshoot it. Some of the graphics and the HMI screens used in this video are from the High-Performance HMI handbook which is a great reference if you want to dig deeper into this topic: bit.ly/3bdWzkM ============================= What is High-Performance HMI? realpars.com/high-performance-hmi High-Performance HMI Design Basics realpars.com/hmi-design Development of High-Performance HMI Philosophy realpars.com/hmi-philosophy ============================= Missed our most recent videos? Watch them here: realpars.com/electrical-grounding realpars.com/isa100-wireless-applications ============================= To stay up to date with our last videos, make sure to subscribe to this YouTube channel: bit.ly/realpars ============================= TWEET THIS VIDEO ctt.ac/99aMd ============================= Follow us on Facebook: facebook.com/therealpars Follow us on Twitter: twitter.com/realpars Follow us on LinkedIn linkedin.com/company/realpars Follow us on Instagram instagram.com/realparsdotcom #RealPars #HMI #PLC




















